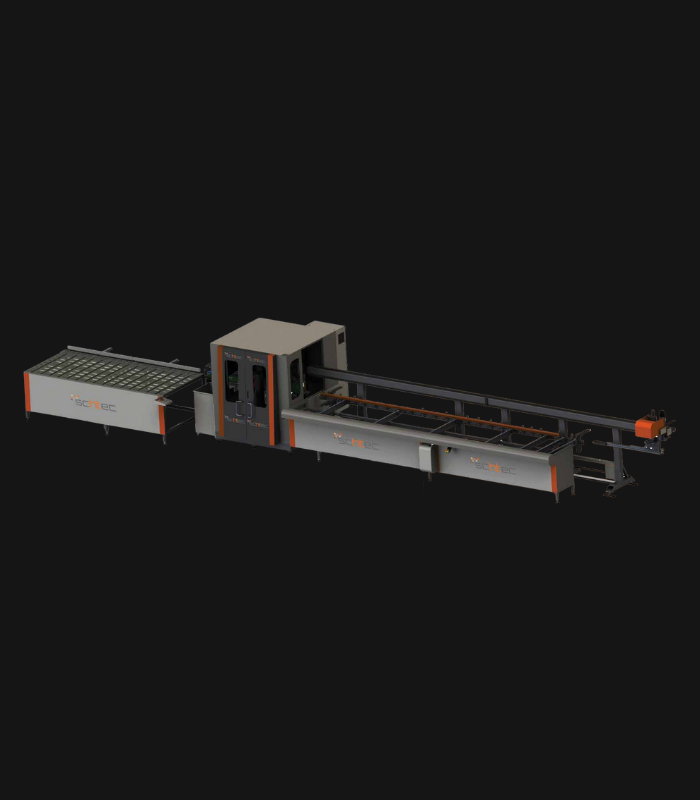
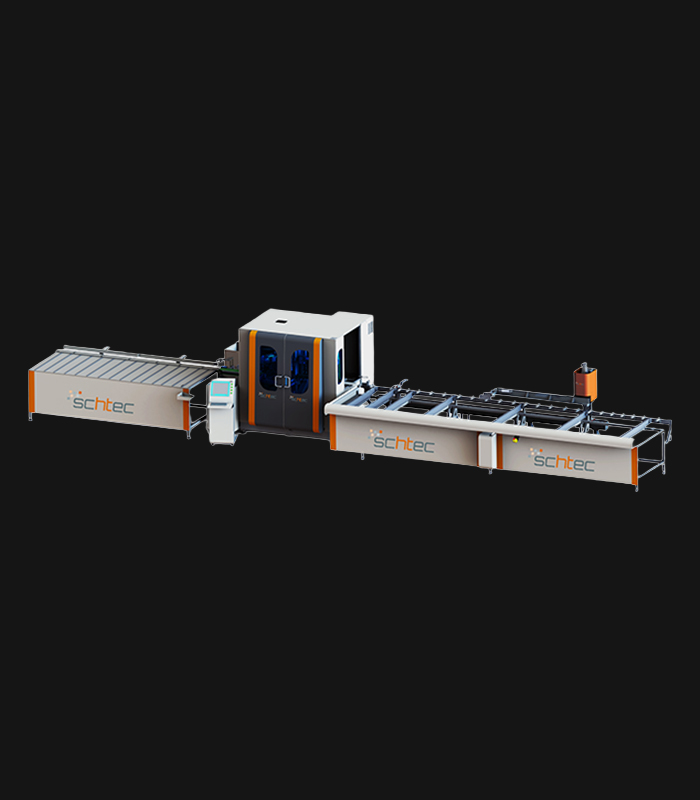
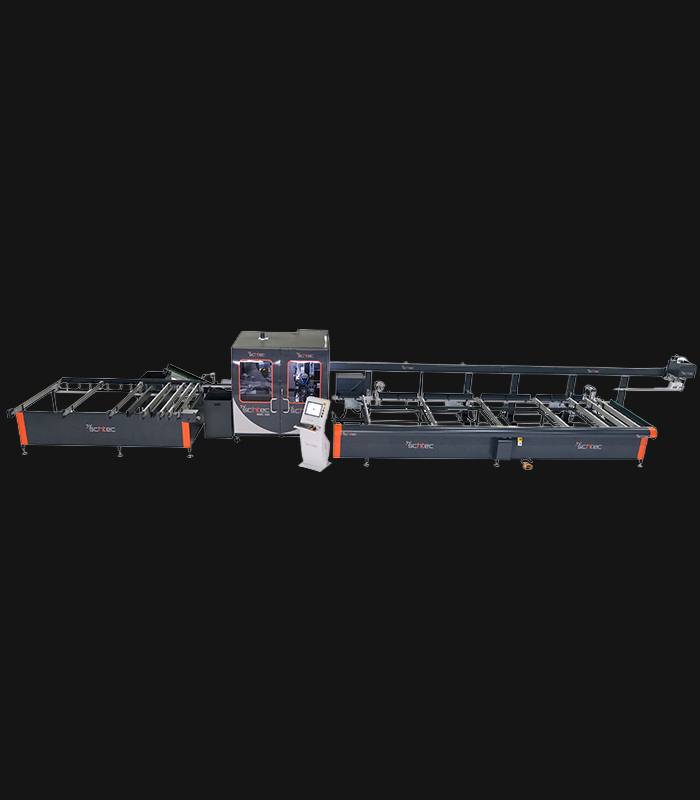
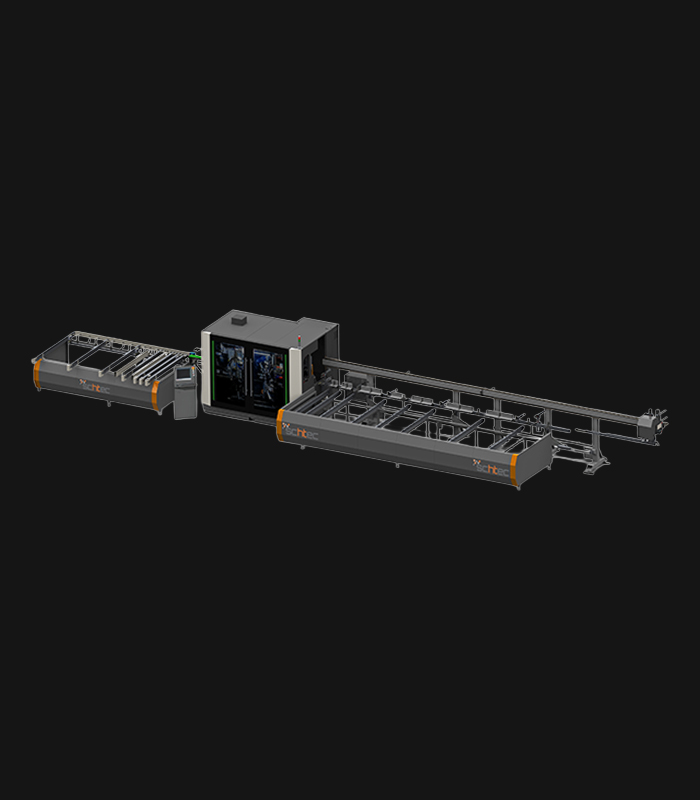
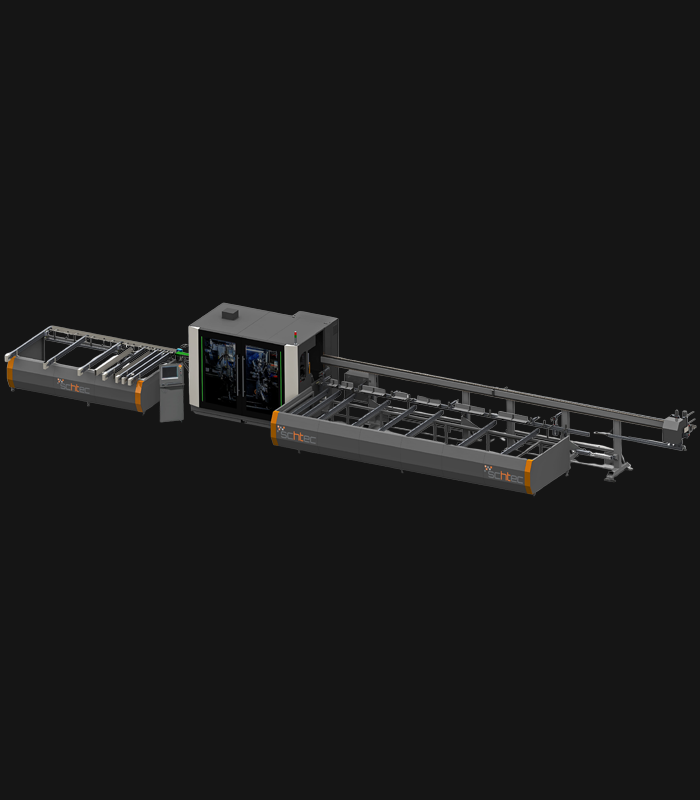
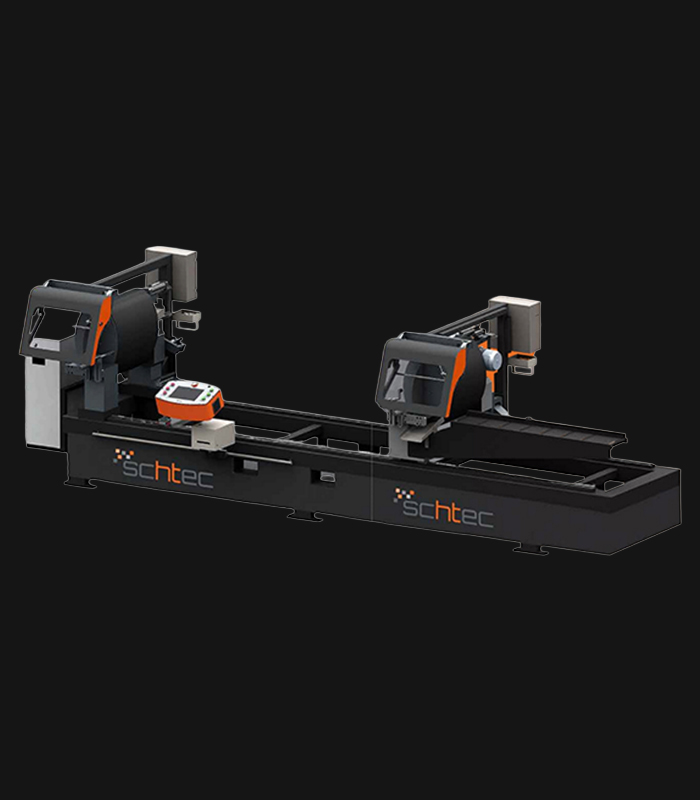
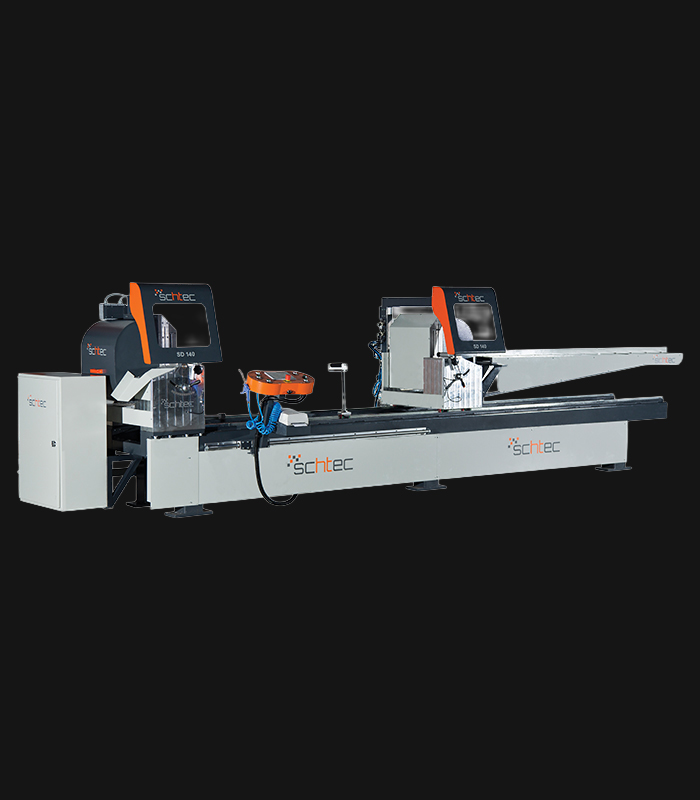
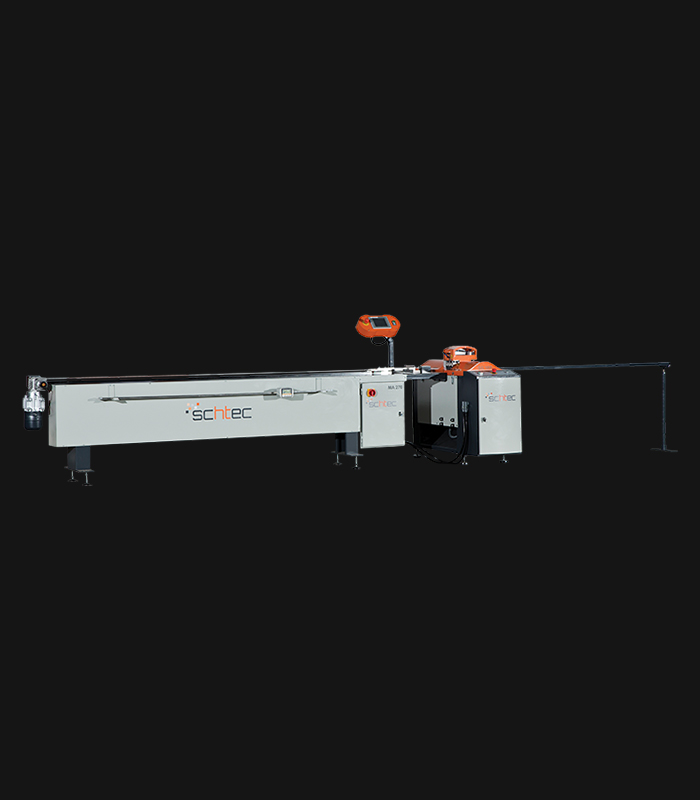
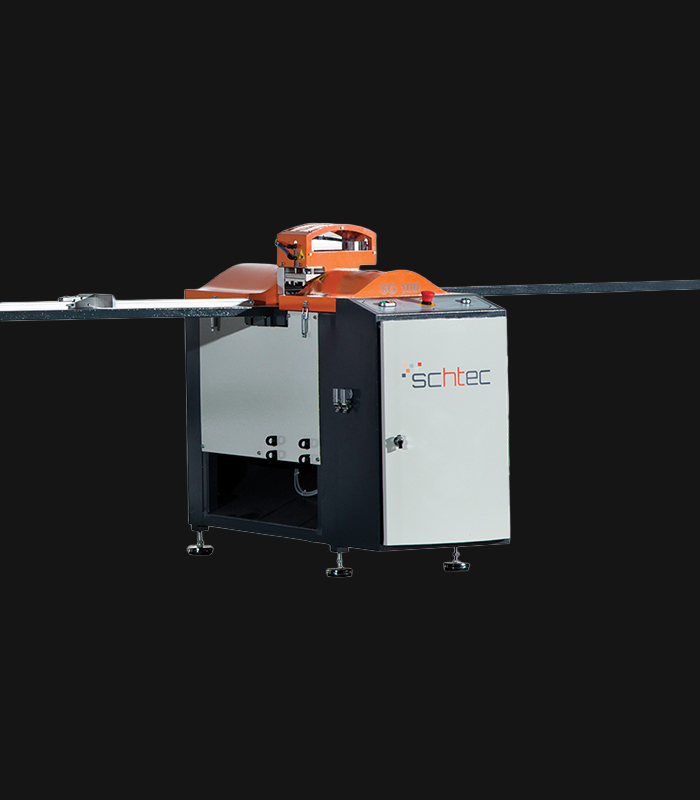
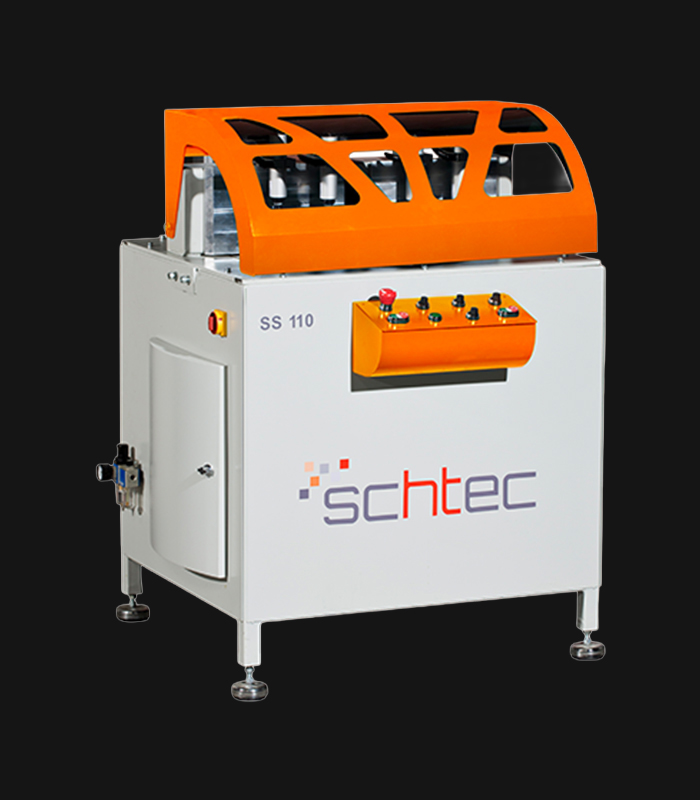
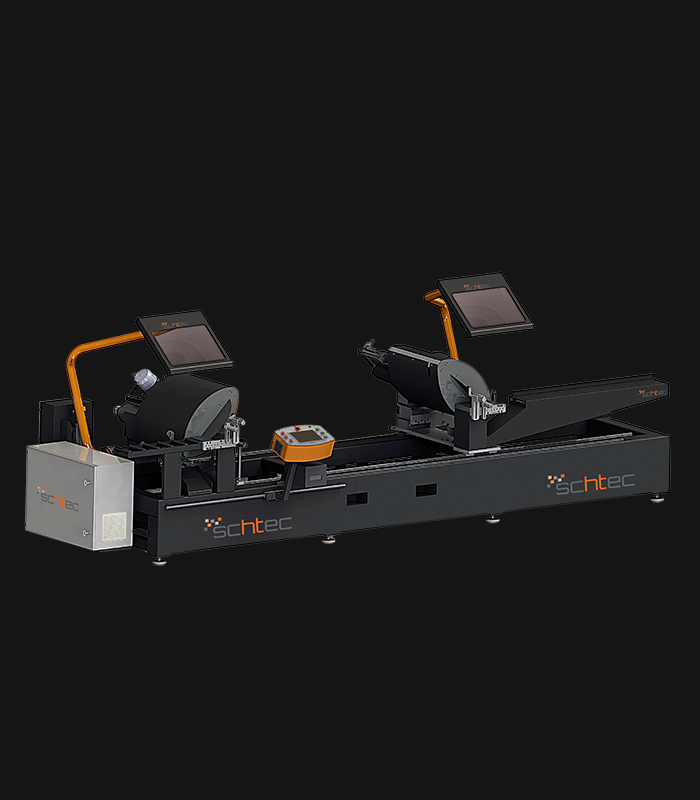
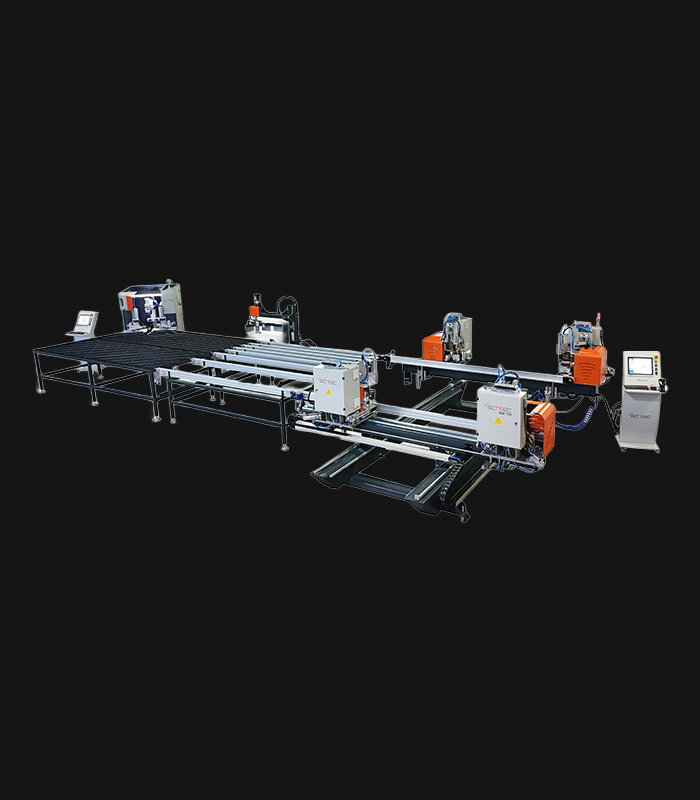
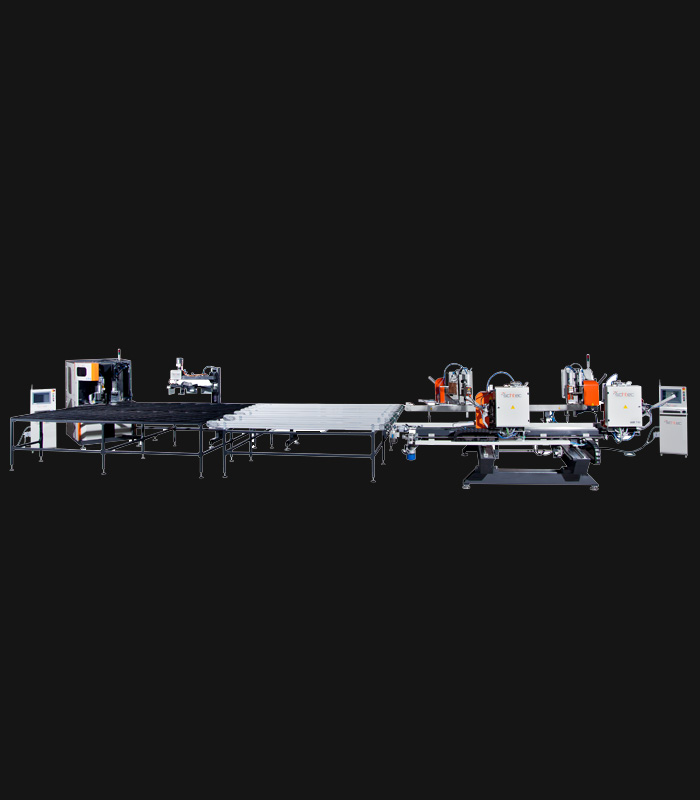
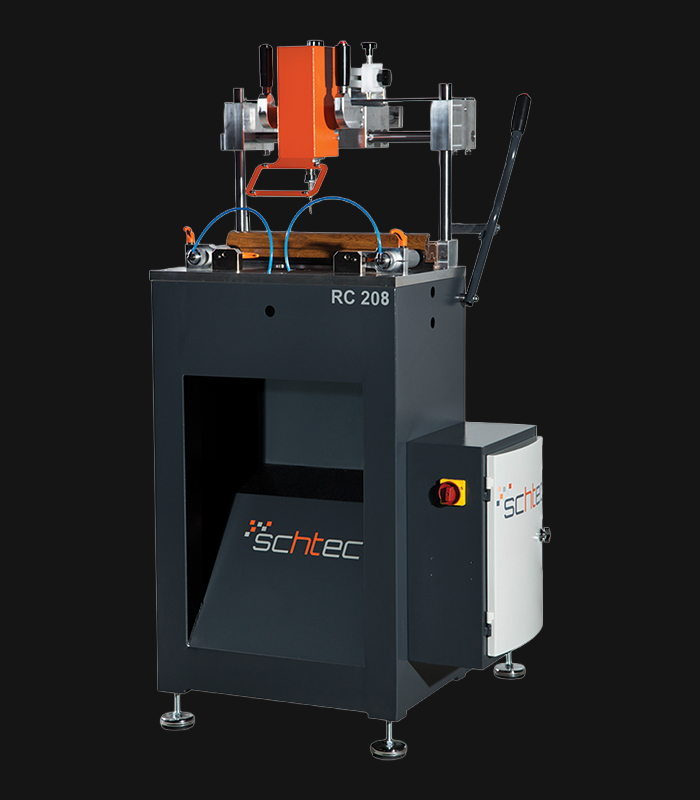
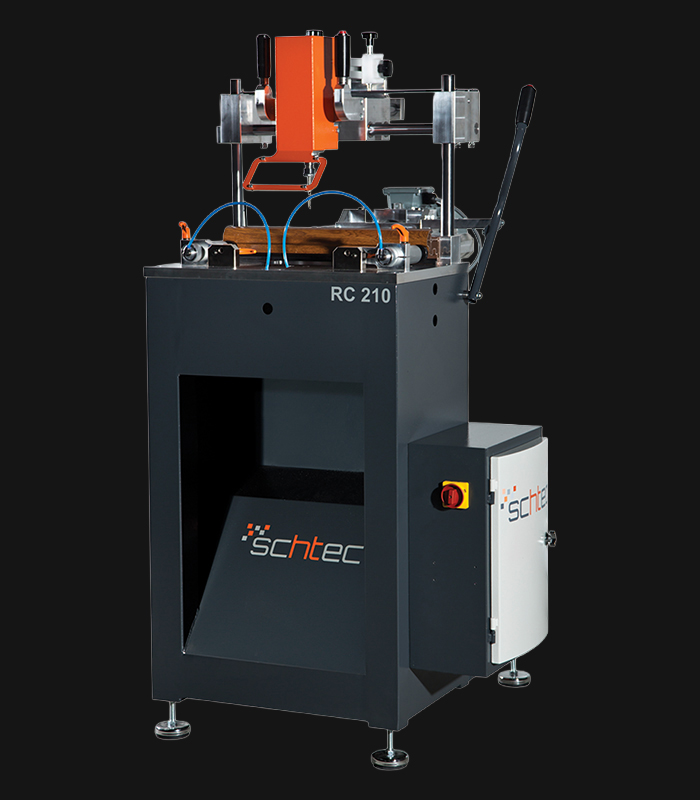
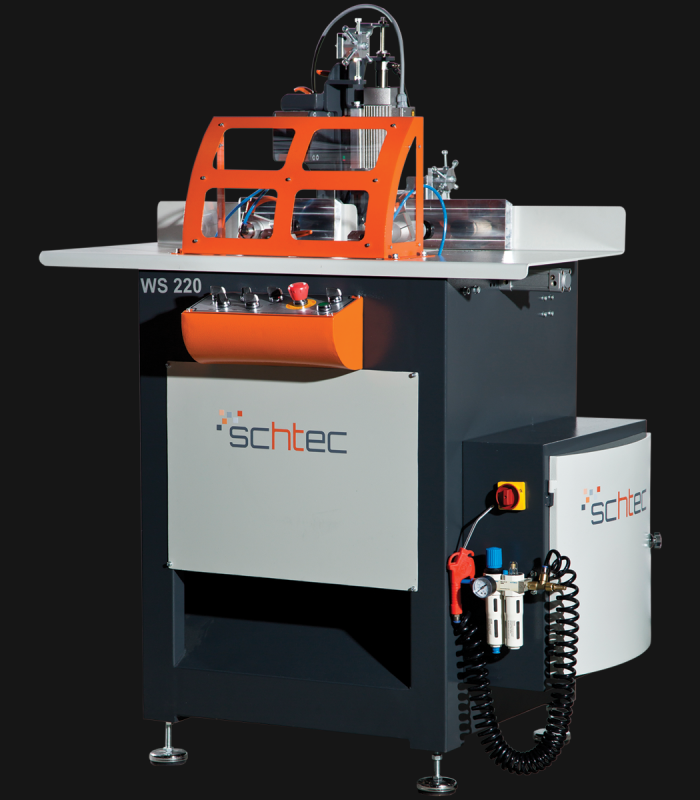
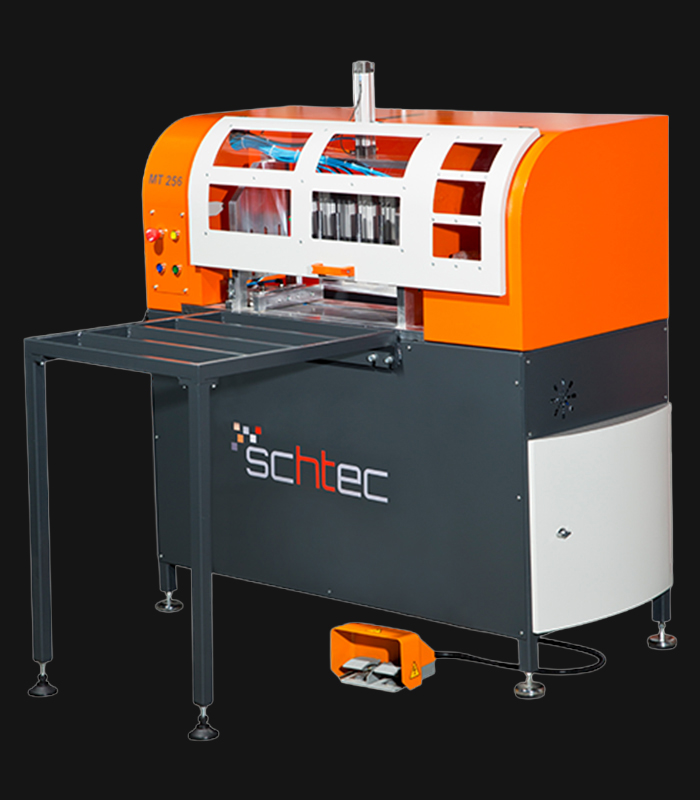
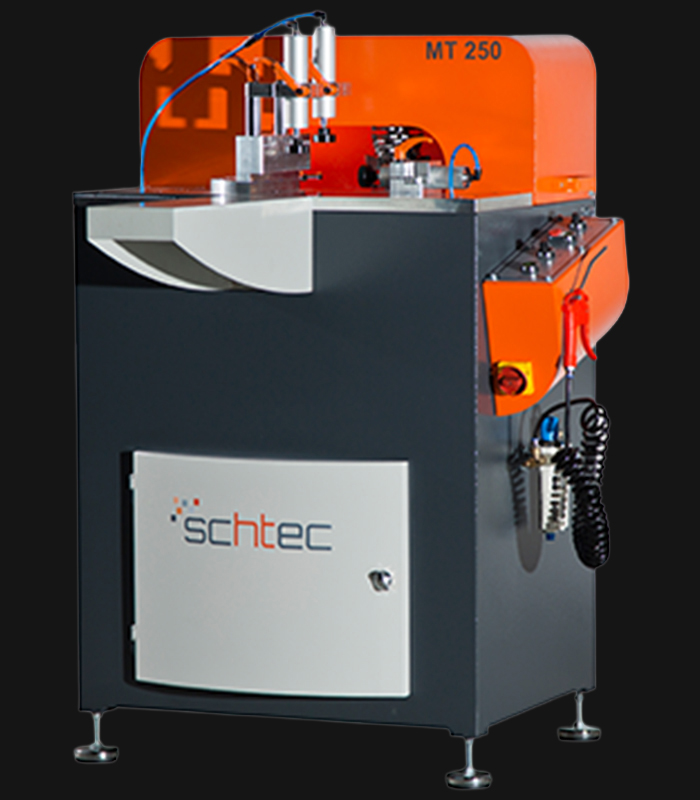
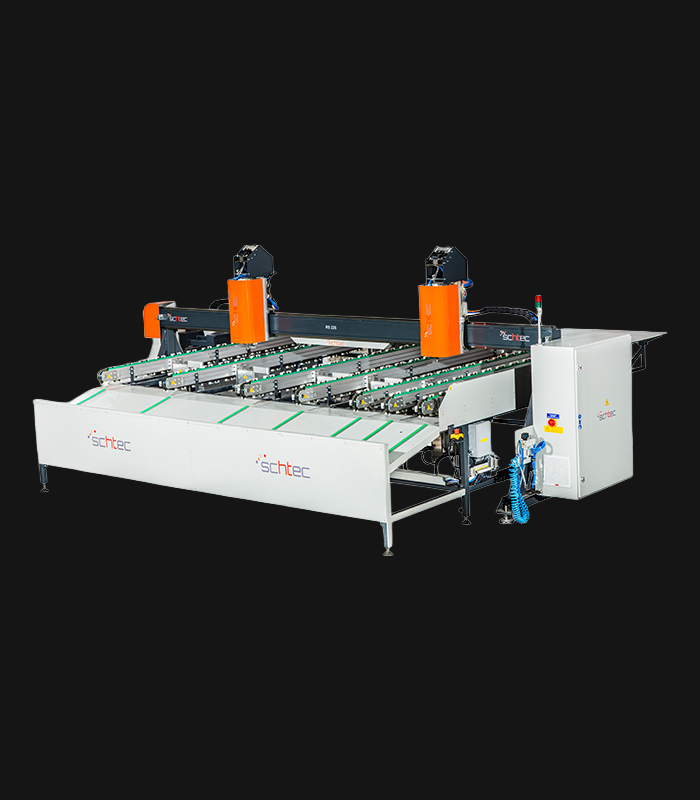
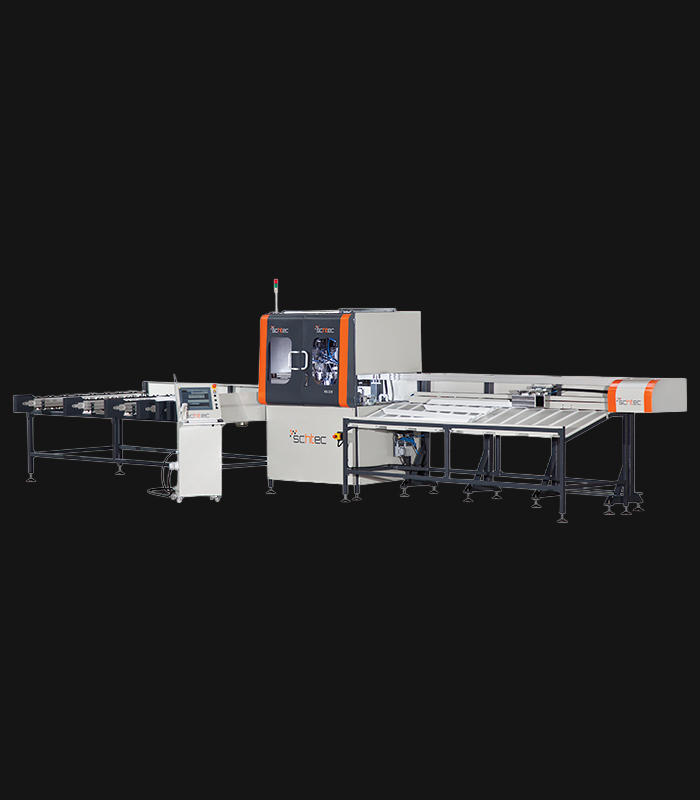
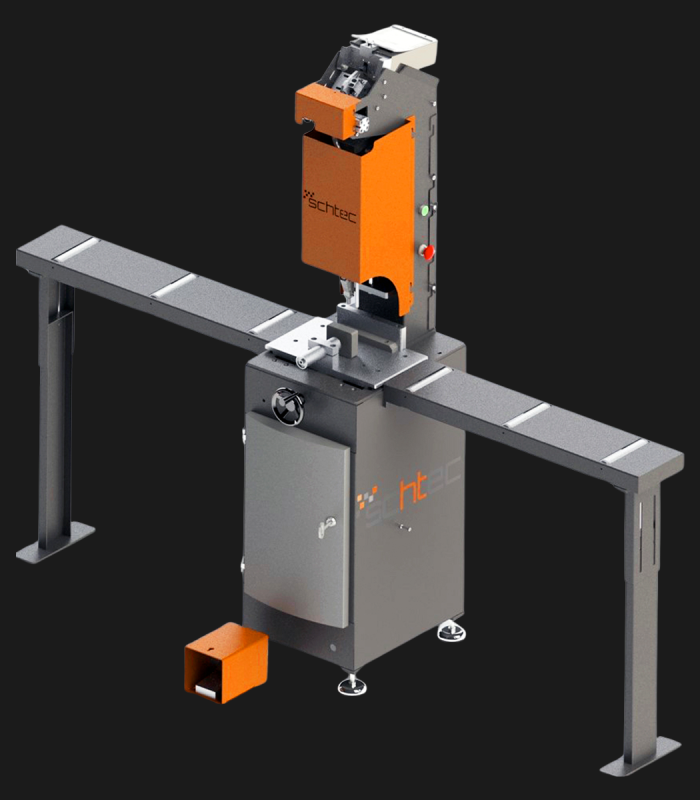
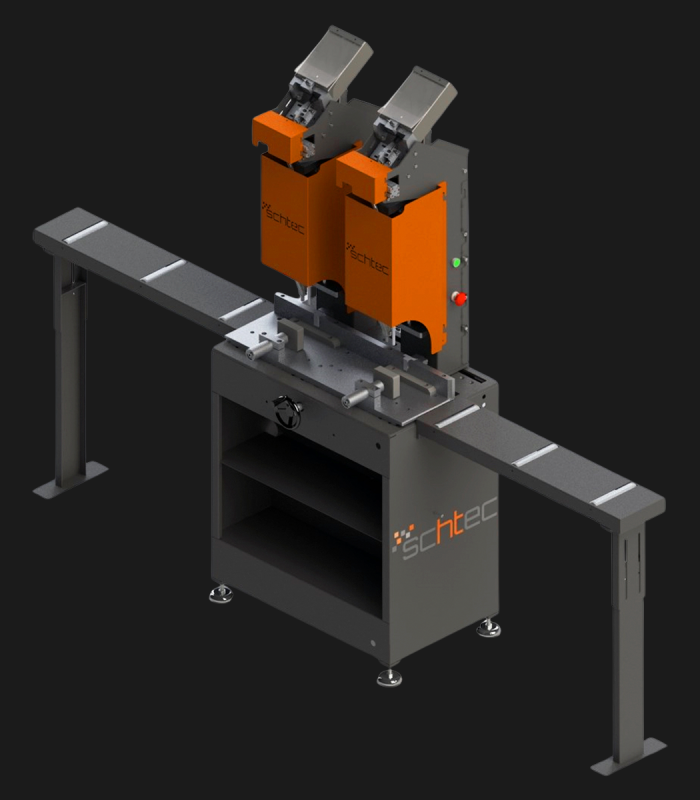
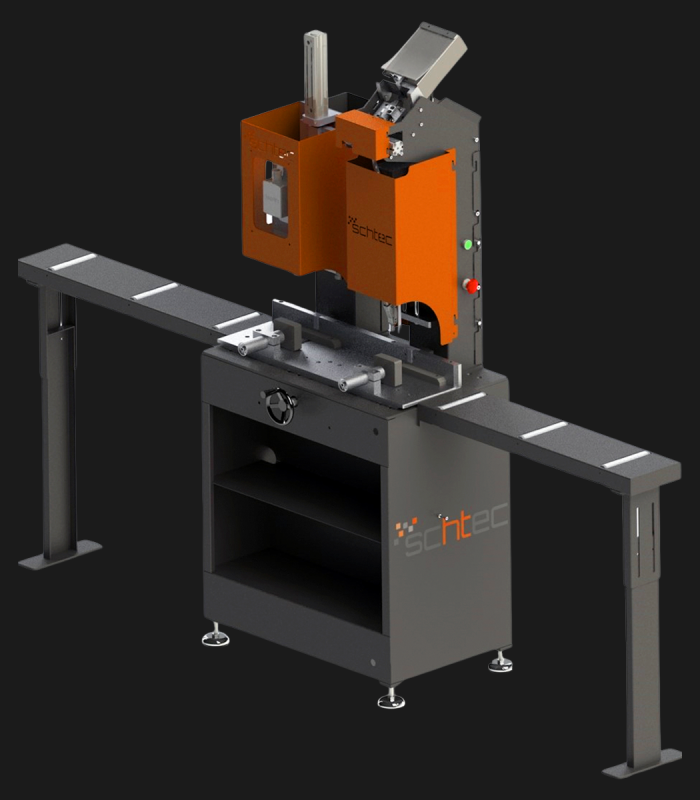
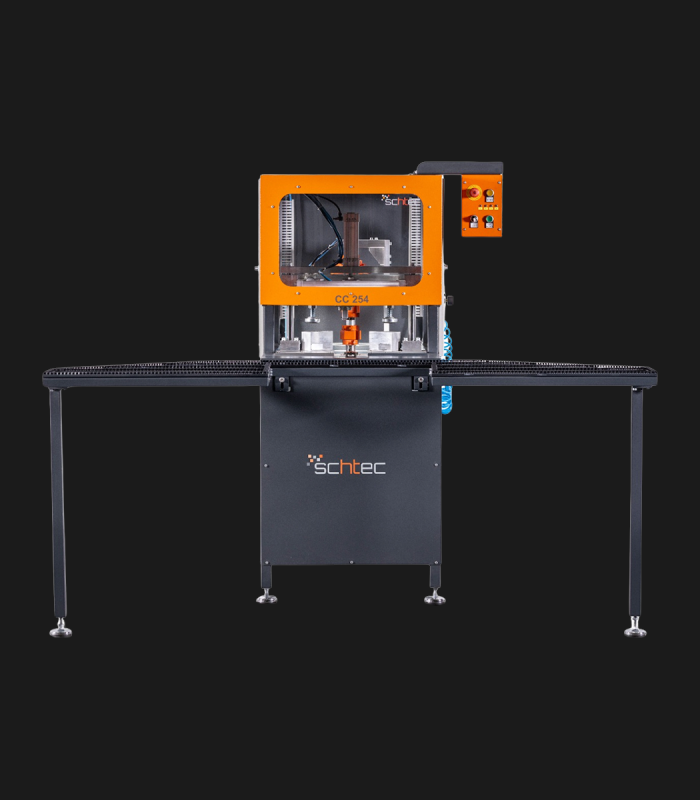
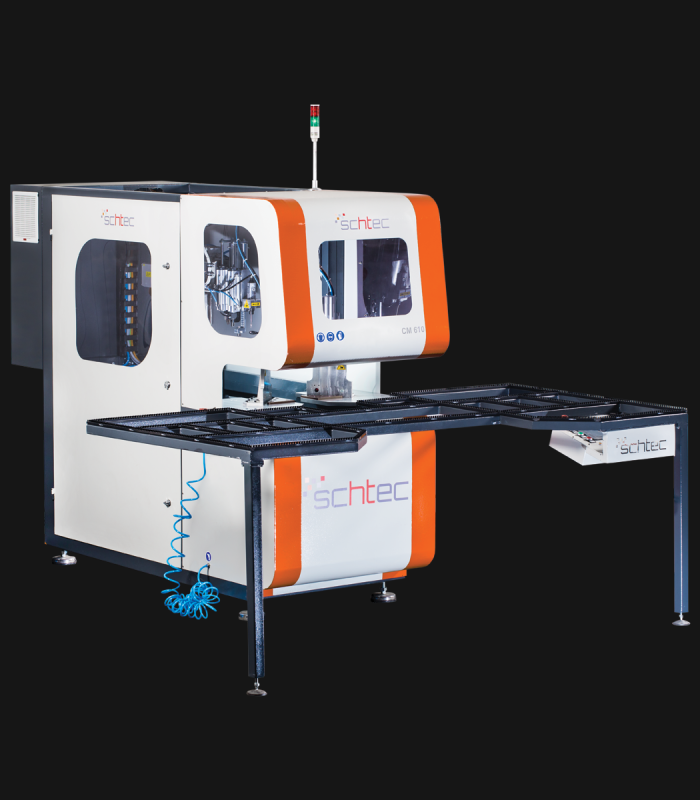
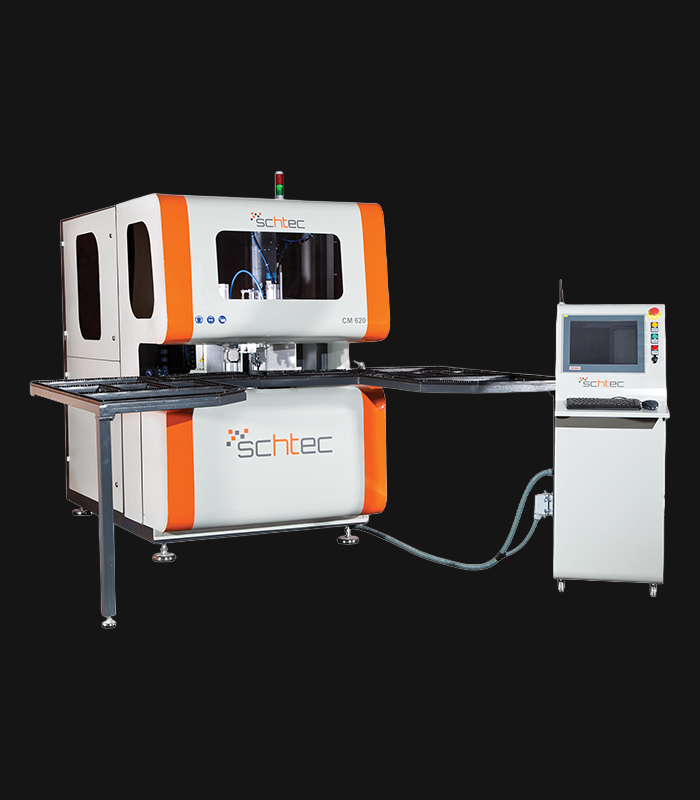
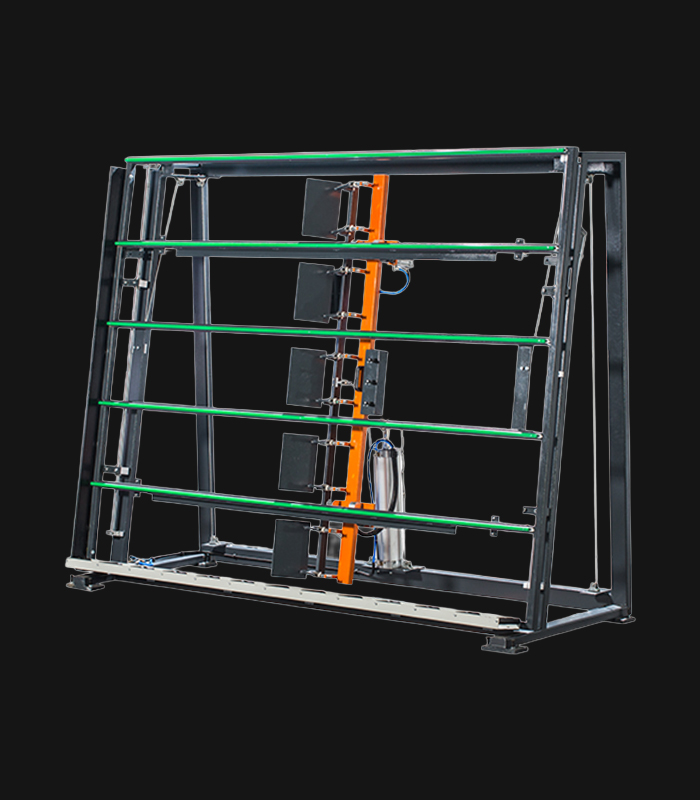
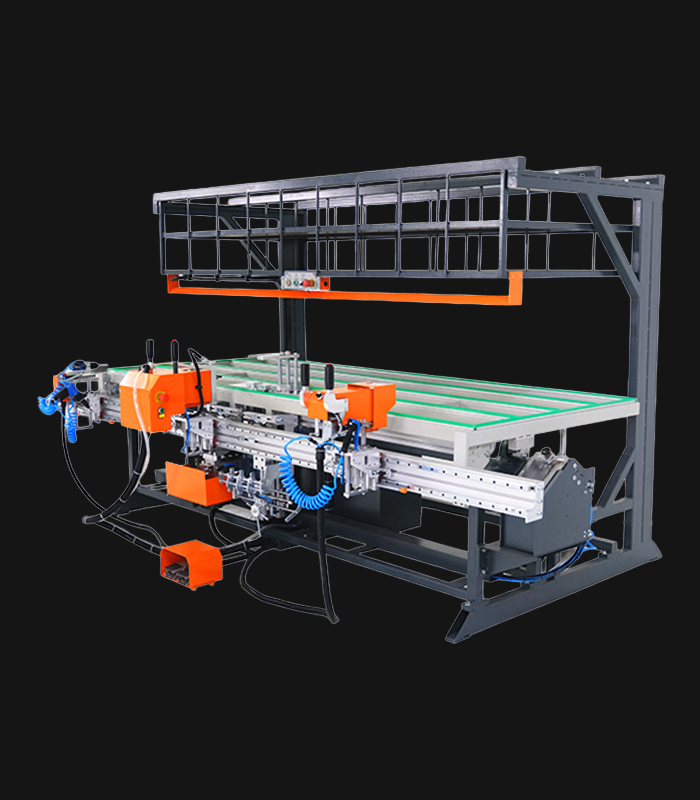
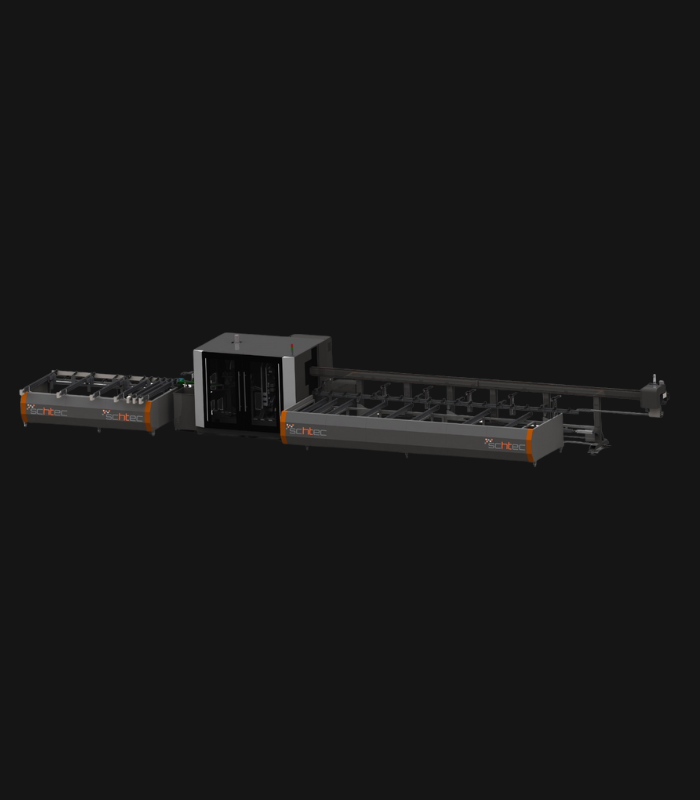
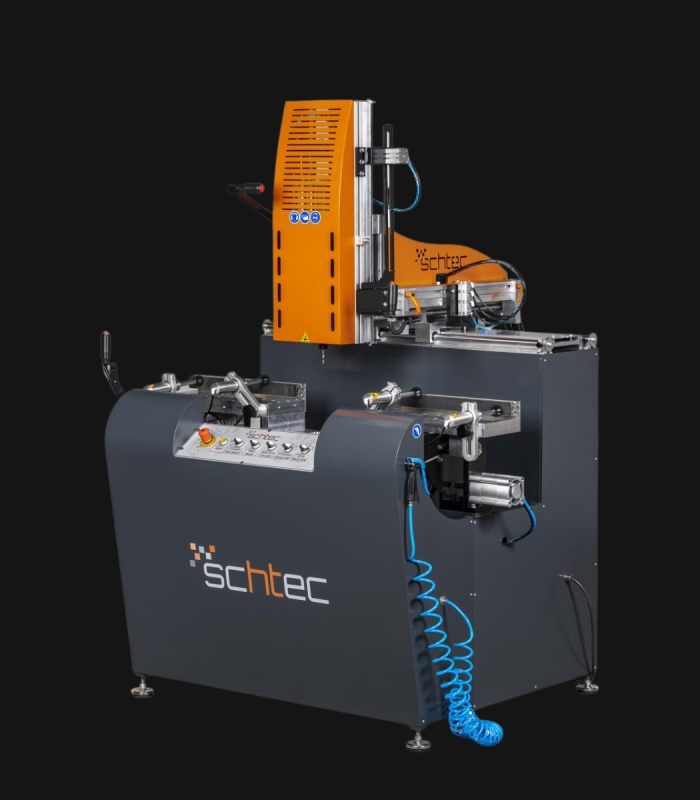
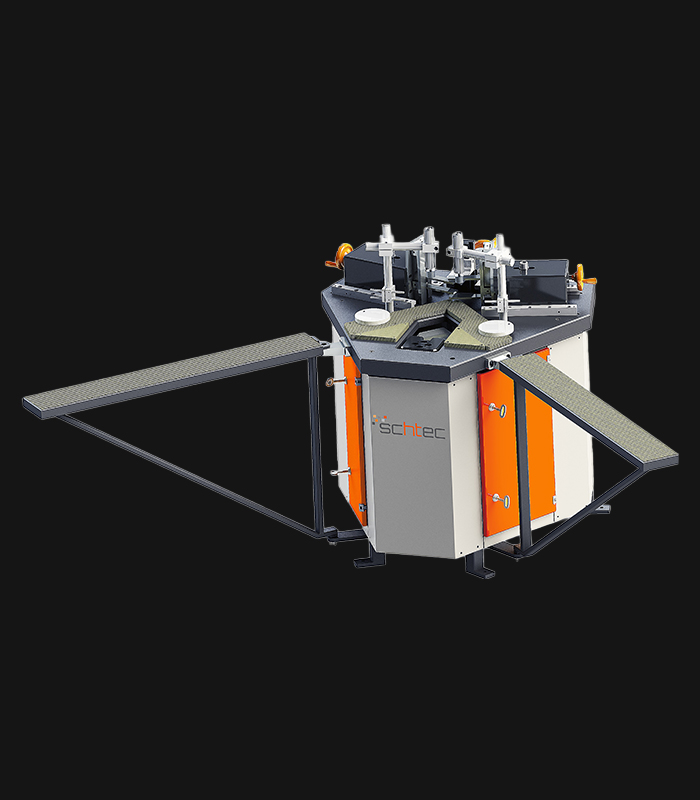
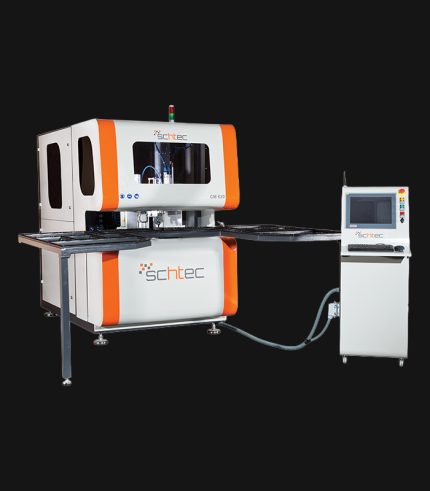
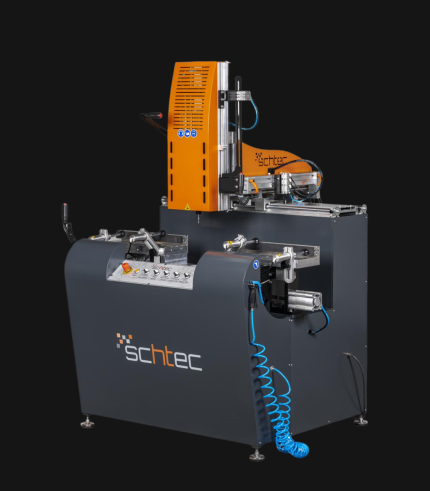
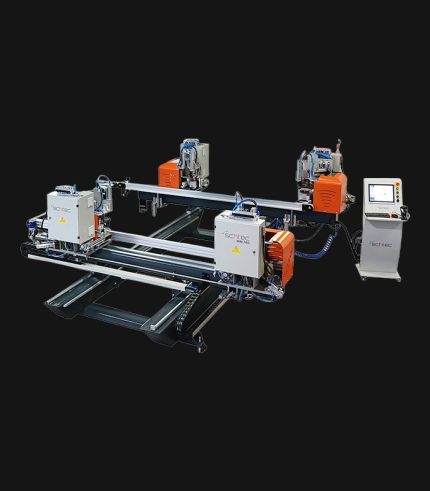
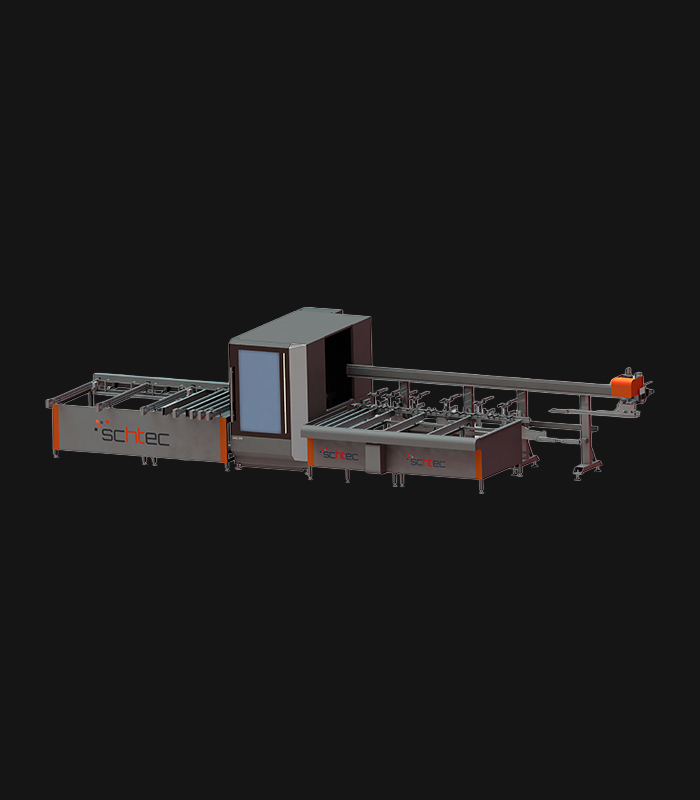
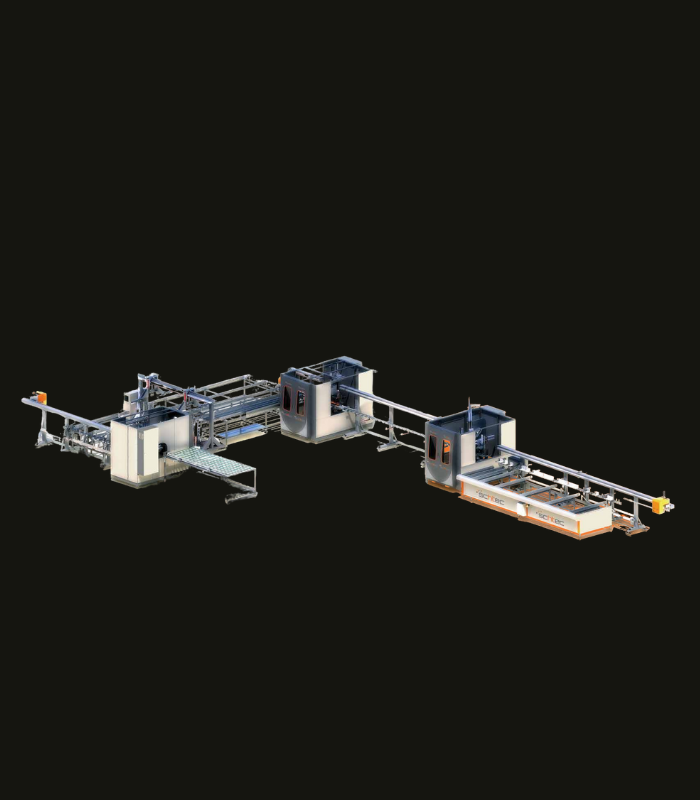
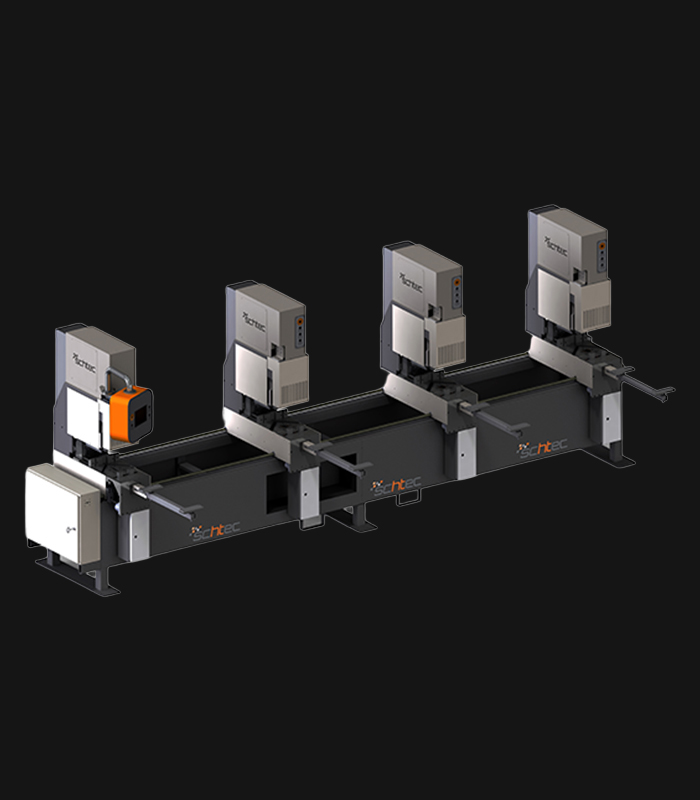
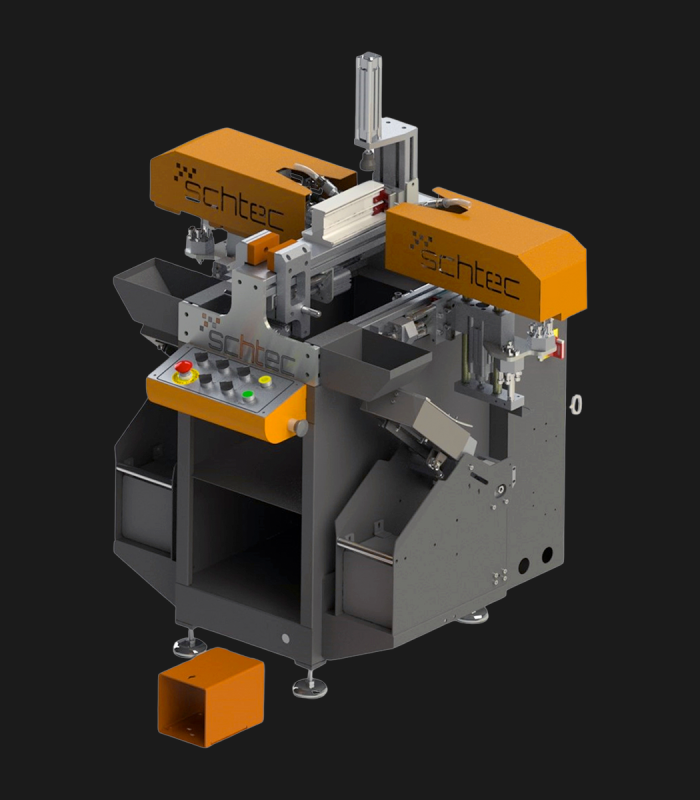
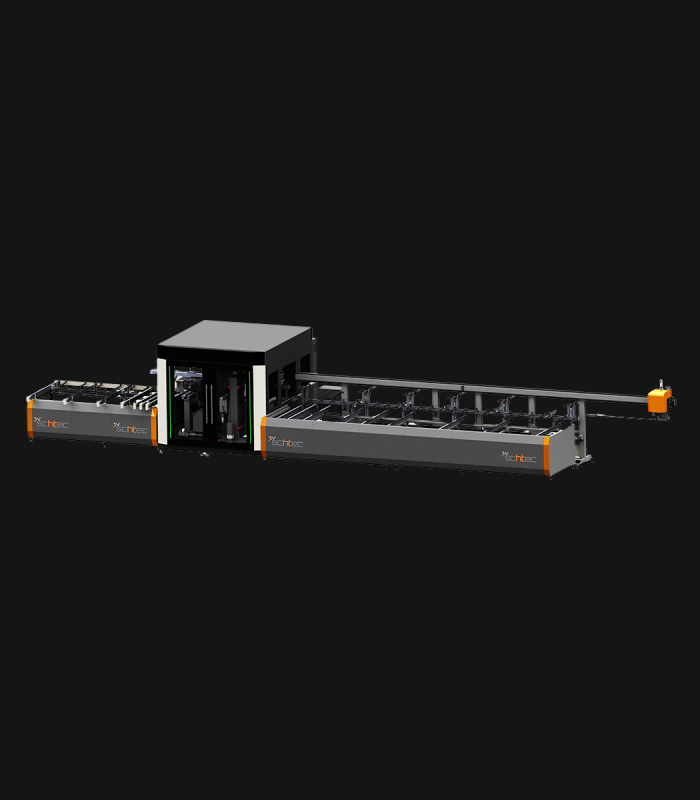
WDV 724 Four Head Inline Welding Machine
Schtec WDV 724: Servo-driven inline 4-head welder for precise PVC frames (45°/90°/V). PID heat & auto centering optimize high-volume production.
WDV 724 Technical Specifications
| Electricity Value | 220-440 V, 3~ 60 Hz |
| Power Consumption | 9 kW, 25 A |
| Min. Welding Size | 320 mm |
| Max. Welding Size | 4500 mm |
| Max. Profile Width | 125 mm (90° Welding Angle) |
| Max. Profile Height | 165 mm |
| Welding Angle | 45°, 90°, and V |
| Air Pressure | 6-8 bar |
| Air Consumption | 200 l/min |
| Machine Length | 5.500 mm |
| Machine Height | 2.100 mm |
| Machine Width | 1.950 mm |
| Machine Weight | 1.980 kg |
SKU:
WDV-724
Category: Welding Machines
Description
Standard Features
- Computer controlled (PID) heat control system to achieve welding strength within standards.
- Precise movement capability thanks to high precision linear guidance systems.
- Temperature, melting and bonding time that can be defined separately for each profile type.
- Ability to select profiles with a pneumatic revolver with 8 different positions.
- Welding heads can weld independently of each other.
- Each head can move independently for 90° and middle registration welding.
- Welding patterns can be changed quickly and easily.
- Height adjustable and foldable profile support system.
- “H” and “T” welding capability.
- Automatic middle register centering system
Optional Features
- 3 or 5 welding head options
Product Description
The Schtec WDV 724 is designed for high-precision PVC frame welding. It performs welding at 45°, 90°, and V-angles using servo-assisted linear guides. PID-controlled heat management, automatic mullion centering, and a pneumatic revolver system enhance efficiency. It can handle H and T-type welds between 320 mm and 4,500 mm, making it ideal for high-volume production lines. With a 9 kW motor and 1,980 kg industrial frame, it ensures long-lasting and efficient performance.
FAQ
Welding Machines
Frequently Asked Questions
Find quick answers to common questions about our Welding Machines.
1. What is the main purpose of a welding machine in PVC manufacturing?
Welding machines like WM 750 Four Head Welding Machine and WD 710 Single Head Welding Machine are used to fuse PVC profile corners by melting material, creating seamless and durable frames. They eliminate the need for mechanical fasteners and ensure air‑ and water‑tight joints. Consistent heat control and pressure maintain structural integrity and appearance over many cycles. In automated lines, welding machines coordinate with cleaning and cutting stations for full process flow.
2. What features should you expect in a high‑performance PVC welding machine?
High‑performance welding machines typically feature servo‑driven axes, parallel welding systems for balanced pressure, PID temperature controllers, and mold parameter storage for multiple profile types. Rapid mold changeover, central lubrication, and Teflon handling systems reduce maintenance downtime. Safety enclosures, light barriers, and efficient air management are also essential. Robust user interfaces and remote diagnostics enhance usability and monitoring.
3. How does the WM 750 Four Head Welding Machine boost productivity?
The WDV 724 is ideal for continuous inline production environments where profiles move through the machine, welding in a flow setup. The WD 720 Double Head Welding Machine is suitable when moderate capacity and flexibility are needed, allowing two corners to be welded simultaneously. Single head machines like WD 710 are good for smaller runs or limited footprint setups. Four‑head machines like WM 740 are preferred for highest throughput in batch production.
4. When would you choose WDV 724 Four Head Inline Welding Machine or WD 720 Double Head Welding Machine?
The WDV 724 is ideal for continuous inline production environments where profiles move through the machine, welding in a flow setup. The WD 720 Double Head Welding Machine is suitable when moderate capacity and flexibility are needed, allowing two corners to be welded simultaneously. Single head machines like WD 710 are good for smaller runs or limited footprint setups. Four‑head machines like WM 740 are preferred for highest throughput in batch production.
5. What maintenance practices ensure durable performance in welding machines?
Clean welding platens, remove residue, and inspect Teflon surfaces regularly to prevent imperfections. Calibrate temperature sensors, PID controls, and servo axes periodically to preserve accuracy. Check pneumatic lines, seals, and air pressure to maintain consistent force during welding. Lubricate motion components and adhere to central lubrication schedules. Monitor error logs, evaluate weld quality, and schedule preventive services to avoid unplanned downtime.